Top 5 AI Tools That Are Transforming Engineer Productivity in 2026
The landscape of software development has shifted dramatically. AI-powered tools have moved from experimental novelties to essential productivity multipliers in engineering workflows. After observing teams across various organizations adopt these technologies, it's clear that certain tools stand out—not just for their technical capabilities, but for their practical impact on daily engineering work.
This post explores five AI tools that consistently deliver measurable productivity gains for software engineers, based on adoption patterns, developer feedback, and real-world performance metrics.
Why AI Tools Matter for Engineering Productivity
Before diving into specific tools, it's worth understanding what makes AI assistants particularly valuable for engineers. Unlike traditional automation that follows rigid rules, modern AI tools understand context, learn patterns, and adapt to individual coding styles. They reduce cognitive load on repetitive tasks while keeping engineers in creative control.
The best AI developer tools share three characteristics: they integrate seamlessly into existing workflows, they learn from your codebase context, and they augment rather than replace human judgment. With that framework, let's examine the top five.
1. GitHub Copilot: The AI Pair Programmer
GitHub Copilot has become the de facto standard for AI-assisted coding. Built on OpenAI's Codex model, it functions as an intelligent autocomplete system that suggests entire functions, complex algorithms, and boilerplate code based on context and comments.
How It Works
Copilot analyzes your current file, understands the programming language and framework you're using, and generates suggestions in real-time. It excels at pattern recognition—if you've written similar code elsewhere, it adapts to your style. The tool supports dozens of programming languages, from Python and JavaScript to Rust and Go.
Real-World Impact
Engineers report saving 20-40% of their time on routine coding tasks. The most significant gains come from generating test cases, writing documentation strings, and implementing standard algorithms. One team at a fintech company reduced their API endpoint creation time from 45 minutes to 15 minutes per endpoint by using Copilot for boilerplate generation.
However, Copilot isn't perfect. It requires careful code review, as suggestions can sometimes include security vulnerabilities or inefficient patterns from its training data. The key is treating it as a junior developer whose work needs oversight, not a senior engineer who can work autonomously.
Best Use Cases
- Boilerplate code generation
- Unit test creation
- API integration code
- Regular expression patterns
- Documentation writing
2. Cursor: The AI-Native IDE
Cursor represents a different approach—rather than adding AI to an existing editor, it rebuilds the IDE around AI capabilities. Built on VS Code's foundation, Cursor integrates large language models directly into the development environment with features like codebase-wide understanding and natural language editing.
Key Capabilities
What sets Cursor apart is its ability to understand entire codebases, not just individual files. Engineers can ask questions about architecture decisions, find where specific logic is implemented, or request refactoring across multiple files. The Cmd+K command palette allows natural language code modifications—describe what you want changed, and Cursor applies it.
Productivity Gains
The codebase understanding feature proves invaluable when working with unfamiliar code. New team members onboard faster by asking contextual questions rather than spending hours tracing through files. Senior engineers use it to identify technical debt patterns across large projects.
A mobile development team reported reducing their feature development cycle from two weeks to nine days by using Cursor for rapid prototyping and refactoring. The AI suggestions were context-aware enough to maintain their existing architectural patterns.
Considerations
Cursor requires sending code context to external servers for analysis, which may not work for organizations with strict data residency requirements. The tool also works best with well-structured codebases—messy, poorly documented code produces less useful suggestions.
Optimal For
- Large codebase navigation
- Refactoring projects
- Learning new frameworks
- Architectural exploration
- Multi-file code changes
3. Tabnine: Enterprise-Grade AI Code Completion
Tabnine serves organizations that need AI coding assistance without sending proprietary code to external servers. It offers both cloud-based and on-premises deployment options, with models that can be trained on private codebases.
Enterprise Features
The standout feature is the ability to run locally or in a private cloud environment. Teams can train custom models on their internal codebases, teaching the AI their specific patterns, naming conventions, and architectural decisions. This creates suggestions that align with organizational standards rather than generic internet code.
Tabnine integrates with all major IDEs and supports team learning—as developers accept or reject suggestions, the model improves for everyone on the team.
Performance Metrics
Organizations using Tabnine's private deployment report a 30% increase in code completion acceptance rates compared to generic models, because suggestions match their specific coding standards. A healthcare technology company reduced security review flagging by 60% after training Tabnine on their security-compliant code patterns.
Trade-offs
The private deployment requires infrastructure investment and ongoing model training. Smaller teams may find the setup overhead not worth the benefits compared to simpler cloud-based alternatives.
Ideal For
- Enterprise environments with security requirements
- Organizations with specific coding standards
- Teams working with proprietary languages or frameworks
- Industries with compliance requirements
- Large engineering teams sharing knowledge
4. ChatGPT/Claude for Technical Problem Solving
While not specifically built for coding, large language models like ChatGPT and Claude have become indispensable for technical problem-solving, architecture discussions, and code review assistance.
Beyond Code Generation
These conversational AI tools excel at explaining complex concepts, debugging logic errors, and exploring architectural trade-offs. Engineers use them as a rubber duck debugging partner that can actually respond with insights. Need to understand a complex algorithm? Want to compare database design approaches? These models provide nuanced explanations with examples.
Claude and ChatGPT are particularly valuable for:
- Understanding error messages and stack traces
- Exploring API documentation and usage patterns
- Generating SQL queries and data transformations
- Writing and debugging regular expressions
- Creating test scenarios and edge cases
Practical Applications
A backend engineering team adopted Claude for code review assistance, having it analyze pull requests for potential issues before human review. This caught 40% of minor bugs and style inconsistencies early, letting senior engineers focus on architectural concerns during actual code review.
Engineers also use these tools for learning new technologies quickly. Rather than reading through entire documentation, they have targeted conversations about specific use cases, getting code examples and explanations tailored to their context.
Limitations
These models lack access to your specific codebase unless you provide context. They also have knowledge cutoffs and may suggest deprecated approaches for rapidly evolving technologies. Always verify suggestions against current documentation.
Best Applications
- Debugging assistance
- Algorithm explanation
- Architecture brainstorming
- Documentation interpretation
- Technical writing and communication
5. Phind: AI-Powered Developer Search
Phind reimagines technical search by combining traditional search with AI-generated answers specifically for developers. Instead of sifting through Stack Overflow threads and documentation, engineers get direct answers with code examples and explanations.
How It Differs
Traditional search returns links; Phind returns solutions. Ask about implementing OAuth in FastAPI, and you'll get a synthesized answer pulling from documentation, Stack Overflow, and GitHub examples, with working code and explanation. It cites sources, so you can verify information and dig deeper when needed.
The tool understands technical context better than general-purpose search. It knows the difference between Python 2 and 3, understands framework versions matter, and tailors responses to your specific stack.
Measurable Benefits
Engineers report reducing time spent searching for solutions by 50-70%. Rather than opening ten browser tabs and piecing together an answer from multiple sources, they get a comprehensive solution immediately. This is particularly valuable for:
- Working with less common frameworks or libraries
- Finding up-to-date solutions for rapidly evolving tools
- Understanding error messages and their fixes
- Discovering best practices for specific use cases
A distributed systems team used Phind to reduce the average time resolving third-party API integration issues from two hours to 30 minutes. The AI synthesis of multiple sources proved more efficient than manual research.
Caveats
Like all AI tools, Phind can occasionally generate plausible-sounding but incorrect solutions. Cross-referencing important implementations remains essential. It also works best for common programming languages and frameworks—niche technologies have less training data.
Prime Use Cases
- API integration research
- Framework-specific questions
- Error message debugging
- Finding updated best practices
- Third-party library usage
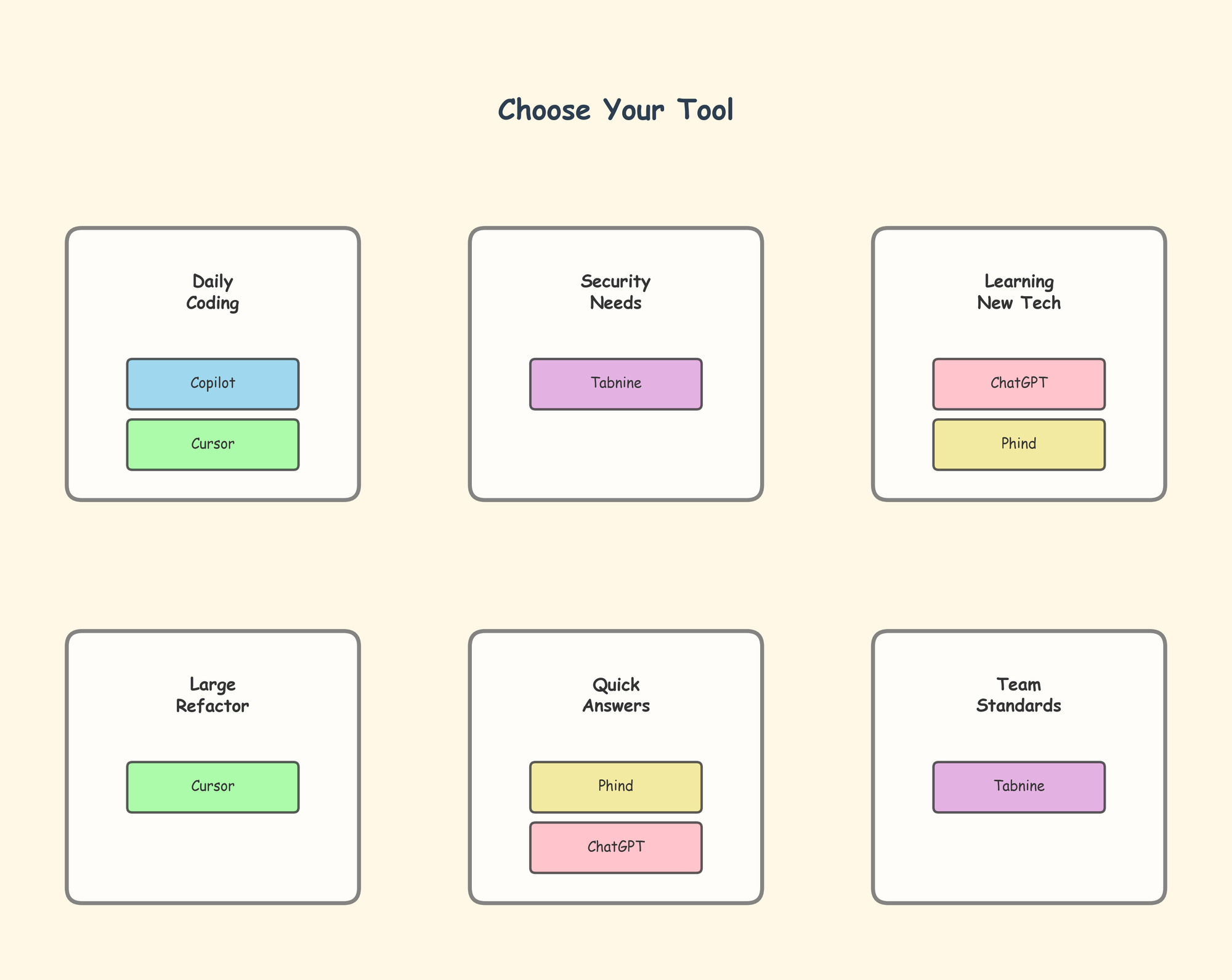
Choosing the Right Tool for Your Workflow
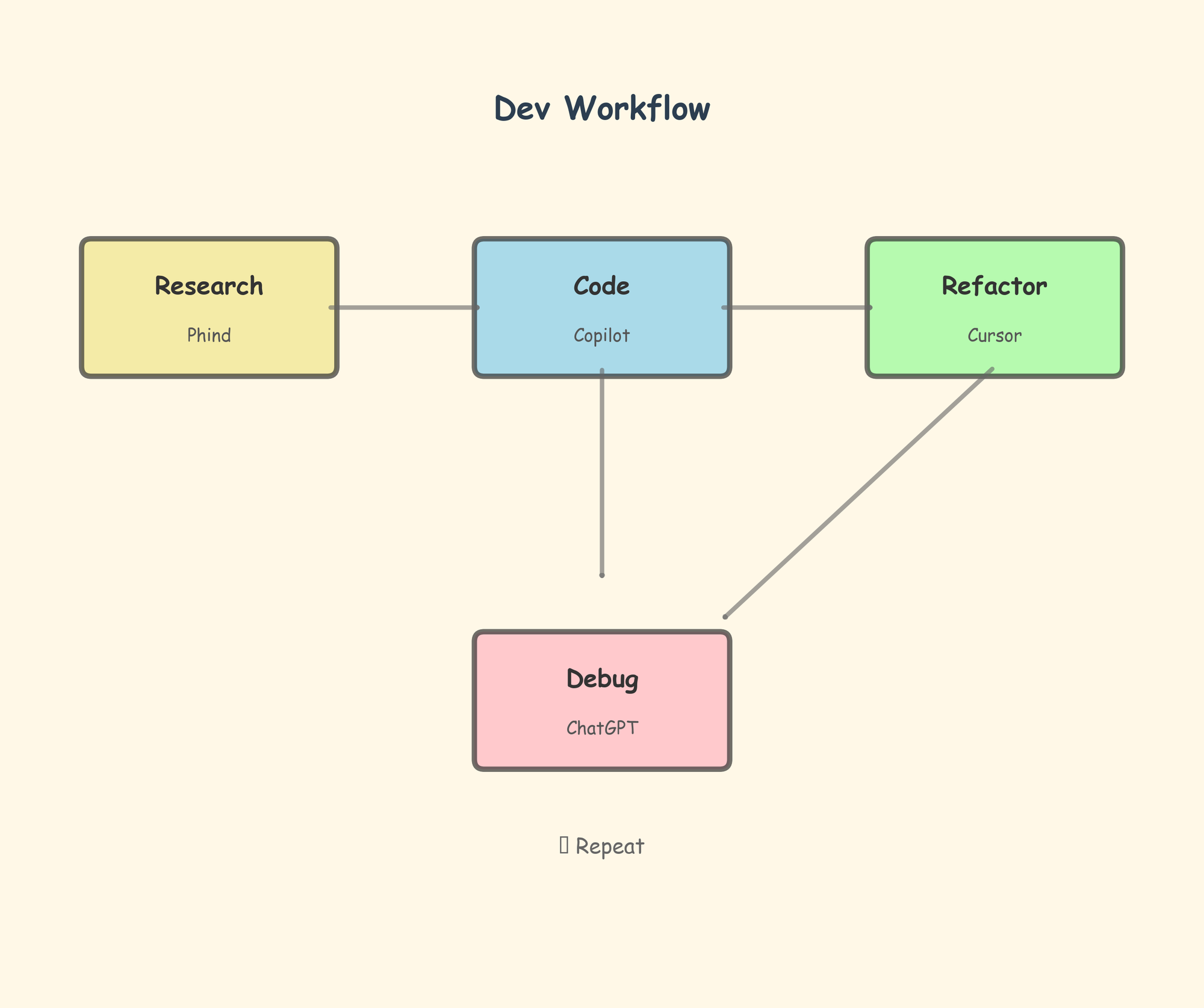
The most productive engineers don't use just one AI tool—they combine multiple tools strategically. A typical workflow might use Copilot for day-to-day coding, Cursor for refactoring sessions, and ChatGPT for architectural discussions.
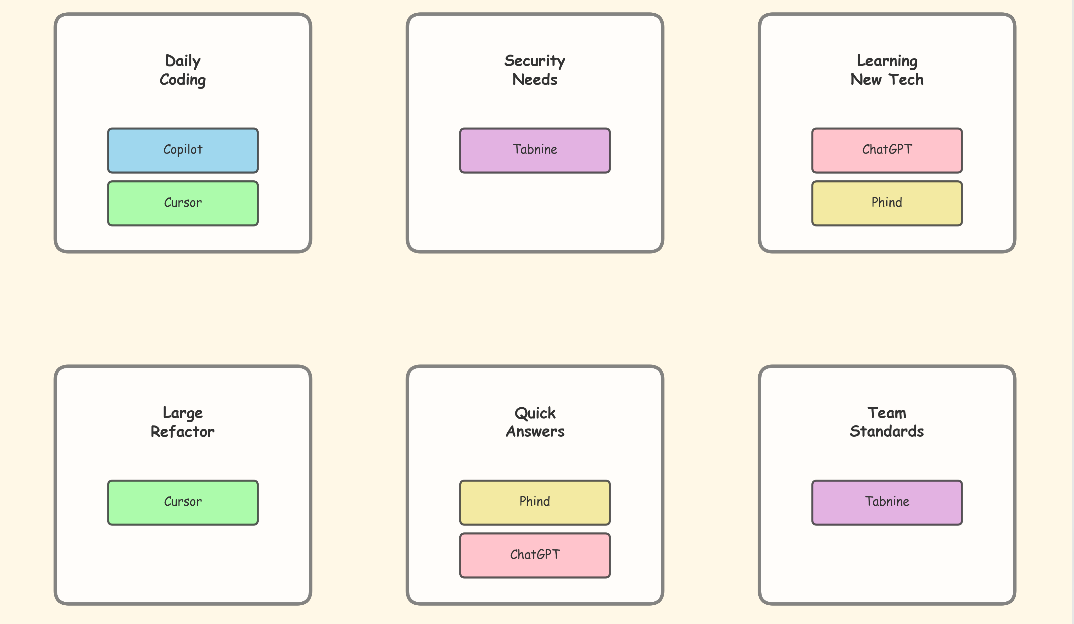
Consider your specific needs:
- Security-sensitive environments: Tabnine with private deployment
- Daily coding efficiency: GitHub Copilot or Cursor
- Learning and problem-solving: ChatGPT or Claude
- Research and documentation: Phind
- Team collaboration: Tools with shared learning like Tabnine
The Productivity Compound Effect
Individual AI tools provide incremental improvements, but the compound effect is transformative. Engineers using these tools report not just faster coding, but reduced mental fatigue, fewer context switches, and more time for creative problem-solving.
A survey across multiple engineering teams found that developers using at least two AI tools consistently were:
- 35% faster at completing feature implementations
- 50% quicker at debugging unfamiliar code
- 60% more confident exploring new technologies
- Significantly less likely to report burnout from repetitive tasks
Implementation Strategy
Introducing AI tools to your engineering workflow requires thoughtful adoption:
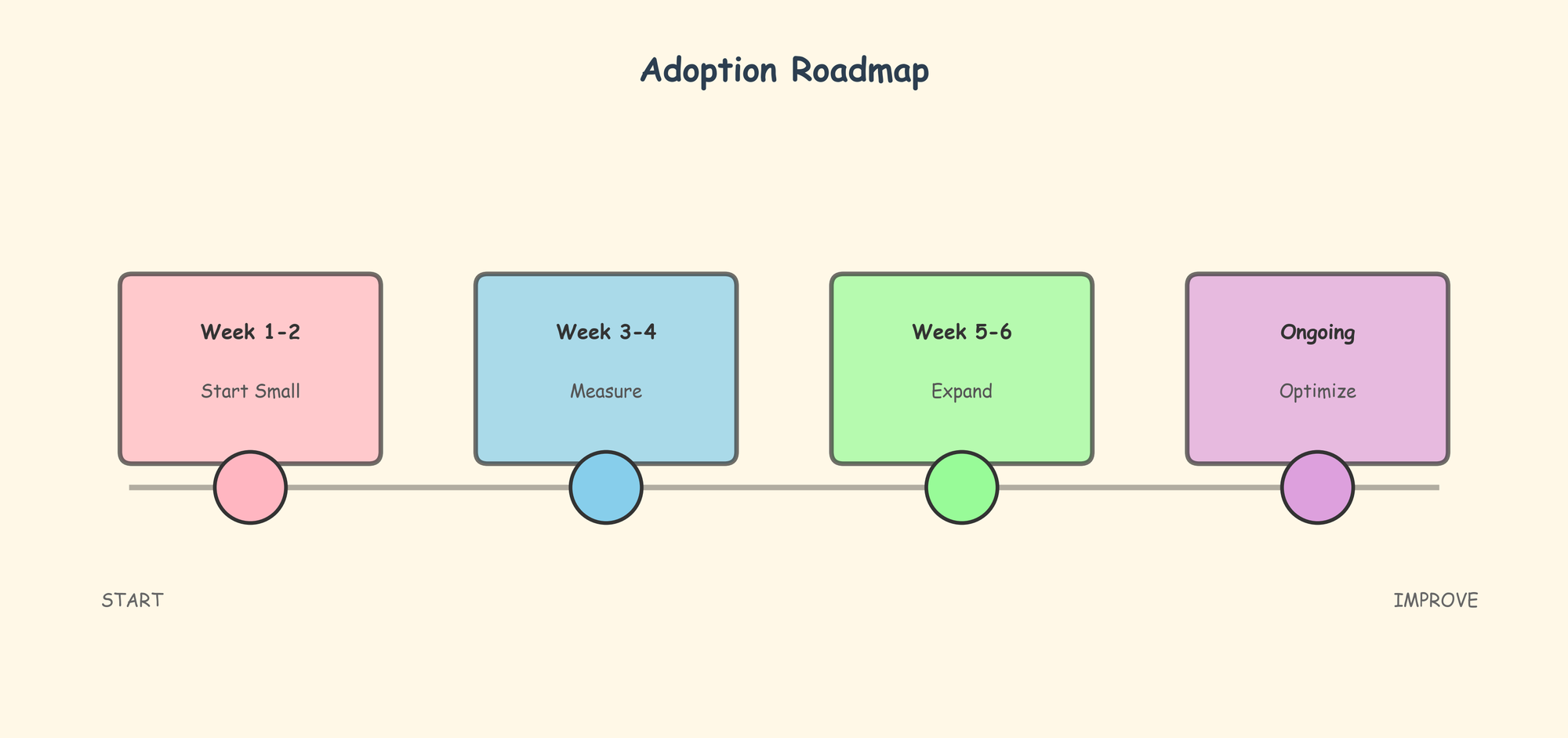
Start Small: Begin with one tool for a specific use case. GitHub Copilot for code completion or Phind for research are good starting points with low learning curves.
Measure Impact: Track metrics like time to complete features, code review cycle time, and developer satisfaction. Quantifying improvements helps justify broader adoption.
Establish Guidelines: Create team standards for AI tool usage, especially around code review processes. All AI-generated code should undergo the same scrutiny as human-written code.
Iterate and Adjust: Different teams find value in different tools. What works for a frontend team might differ from a data engineering team's needs.
Stay Current: The AI tool landscape evolves rapidly. Allocate time quarterly to evaluate new tools and updates to existing ones.
Looking Forward
AI tools for engineers have moved past the hype phase into practical productivity enhancement. The tools highlighted here represent the current state of the art, but the field continues advancing rapidly. We're seeing emerging capabilities like AI-powered code review, automated technical documentation generation, and intelligent bug prediction.
The engineers who thrive in this new landscape won't be those who resist AI tools or those who blindly accept every AI suggestion. Instead, success comes from developing good judgment about when and how to leverage AI assistance—treating these tools as powerful instruments that amplify human creativity and engineering judgment.
The question is no longer whether AI tools improve engineering productivity—the data clearly shows they do. The question now is how to integrate them thoughtfully into your specific workflow to maximize their impact while maintaining code quality, security, and team collaboration.
What AI tools have made the biggest difference in your engineering workflow? The landscape evolves quickly, and practical experience from the developer community continues shaping which tools deliver real value versus those that merely promise it.